Differences in Network Cable UTP Straight and Crossover

UTP
cable transmission medium is one of the most widely used to create a
local network (Local Area Network), but because the price is relatively
cheap, easy to install and quite reliable. As the name implies Unshielded Twisted Pair means twisted pair cable / twisted (twisted pair) without protective (unshielded). This convolution function is as elimination of the induction and leakage. Previously there was also cable STP (Shielded Twisted Pair), for example the picture can be seen below:There
are several different categories of UTP cable that shows quality, the
number density of winding pairnya, the higher the katagorinya closer the
windings and other parameters such as the following: UTP cable Category
1 Used for telephone communication (transmits low-speed data), so as
not cocock to transmit data , UTP
cable Category 2 Capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 4 Mbps
(Megabits per second) cable UTP Category 3 is used in 10BaseT network,
capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 1Mbps. 10BaseT stands 10 Mbps, Baseband, Twisted pair. Cable
UTP Category 4 Often used in token ring topology, capable of
transmitting data at speeds up to 16 Mbps UTP Category 5 capable of
transmitting data at speeds up to 100 Mbps, cable UTP Category 5e
capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 1000 Mbps (1Gbps),
frequency signal which can be passed to 100 MHz. Category
6 UTP cable Capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 1000 Mbps
(1Gbps), frequency signal that can be passed up to 200 MHz. Physically there is a separator which is made of plastic that serves to separate the four pairs in the cable. Category 7 UTP cable gigabit Ethernet (1Gbps), signal frequency of 400 MHzIn
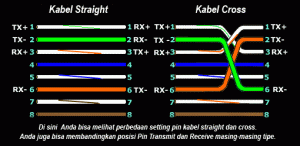
the lan network using Ethernet or commonly known two types of network
cables that STRAIGHT and CROSS, both of which have different functions
in the network connectivity. STRAIGHT cable generally used for mengghubungakan connections from
Port on Switch / Hub, and CROSS cable is used for point to point
connection between two computers connected via ethernet card.To
distinguish and STRAIGHT CROSS cable is to look at the color
arrangement of pins on the connectors RG 45 which consists of 8
different colors. I'll explain how to prepare the most common colors used for cable termination Straight and Cross (Standard International). 8
colors normally used are Orange (O), White Orange (PO), Blue (B), White
Blue (PB), Green (H), White Green (PH), Brown (C), White Chocolate
(PC). for some kind of specific quality cables typically only use a single
color for all the pins, you must be extra careful to conduct this type
of cable termination.1. Cable STRAIGHTTo perform a straight cable terminations usually several ways to apply
the twin side which likens the arrangement between the two ends of the
connector without regard to the arrangement of colors used.
we use here is the arrangement of colors according to international
standards, why do I say international standards, because in the basic
curriculum standards are applied cisco academy is sure to be used and as
a basic knowlegde for a network technician or engineer one spot is
absolutely understandable.
As for the function of each pin can be seen in the picture below
Examples of the use of a straight cable is as follows: Connect the
computer to connect the computer to a LAN switch on the cable modem /
DSL router with a LAN Connecting the cable modem / DSL router Connecting
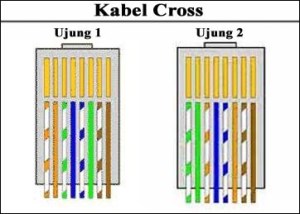
switches to connect the hub to the router2. Cable CROSSIf the termination of the CROSS cable you are not using prescribed
standards or because the cable that you use only has one color for each
pinya, you must remember is the sequence.cros
cable is a cable that has a different color sequences at both ends of
the connector, any arrangement that distinguishes her? from
the arrangement of the colors that you have you just swap the stacking
order of pin / color at one end of the connector that you plug in which
the sequence of colors that are exchanged with the sequence 1 to 3 and
the sequence of colors to 2 with the 6th. (1.3) (2.6), then its results as follows:
As for the function of each pin can be seen in the picture below
Examples of the use of cross-over cable is as follows:
- Connecting two computers directly
- Connect two pieces of switch
Connect two pieces of hub
- Connect a switch with a hub
- Connect the computer to the router
8 pieces of existing wires in the UTP cable (either on a straight or cross-over cable) only four pieces are used to send and receive data, ie no cables on pins 1,2,3 and 6.
Creating Straight and Cross Over Cable
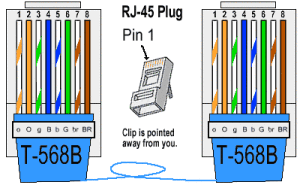
To create a wired network using UTP cable, there are some tools that we need to prepare, the UTP cable, RJ-45 Connector, crimping tools and RJ-45 LAN Tester, sample picture as below:
Practice makes cable Straight:
- Peel the end of the UTP cable, approximately 2 cm
- Open spiral cable, align the cable and sort according to the standard TIA / EIA 368B
- After the order according to the standard, cut and flatten the ends of the cable,
- Put the cable is straight and parallel into the RJ-45 connector, and make sure all the wiring position is correct.
- Perform crimping using a crimping tool, press the crimping tool and make sure all the pins (brass) on the RJ-45 has "bite" each cable.
- Once completed at the end of that one, do it again on the other end
- The final step is to check the cable that you created earlier by using the LAN tester, how inputs each end of the cable (RJ-45) to masing2 an available port on the LAN tester, turn it on and make sure all the LED lights up in accordance with the order of cable that we created.
- Below is an example of the end of the UTP cable that has an RJ-45 connector is installed properly, the cable sheath (blue) come into the connector, cable order from left to right (in the figure below pin cable sequence starting from top to bottom).